Training foundations for reliable leash and recall behavior
Reliable leash and recall skills are built from consistent, positive training foundations that fit your dog’s temperament and lifestyle. This article covers core principles for leash manners and recall, practical step-by-step progressions, how behavior and enrichment support learning, and common challenges owners face when teaching dependable responses.

Good leash manners and a dependable recall start with clear expectations, consistent routines, and stepwise teaching that respects a dog’s learning pace and motivation. Initial sessions should focus on short, high-value interactions that reward correct choices and gradually increase distractions. Combining training with attention to wellness areas such as nutrition, exercise, and dental and grooming routines helps a dog stay physically and mentally ready to learn.
Training approaches for leash work
Different training approaches—clicker training, marker words, or simple praise and treats—can all produce reliable leash behavior when applied consistently. Begin indoors or in a low-distraction yard with a loose-leash criterion: mark and reward the moment the leash goes slack rather than waiting for a perfect extended walk. Short, frequent sessions (5–10 minutes, several times a day) build momentum. Use reinforcement schedules that shift from continuous rewards to intermittent reinforcement so the behavior persists. Tools such as front-clip harnesses can reduce pulling while you teach the desired walking behaviors, but they should not replace training.
How behavior influences recall success
Recall is a behavior built on reliable attention and strong motivation to return. Dogs will weigh the value of what they are doing against the reward for coming back. Prioritize high-value rewards during early recall training—special treats, play, or access to something desirable. Train recall at increasing distances and distractions: start in the home, move to the yard, then to a quiet park, and finally to places with higher stimulus levels. Avoid calling a dog only to deliver something unpleasant (like a bath) as that undermines trust. Maintain consistent cues and celebrate recalls so returning is consistently rewarding.
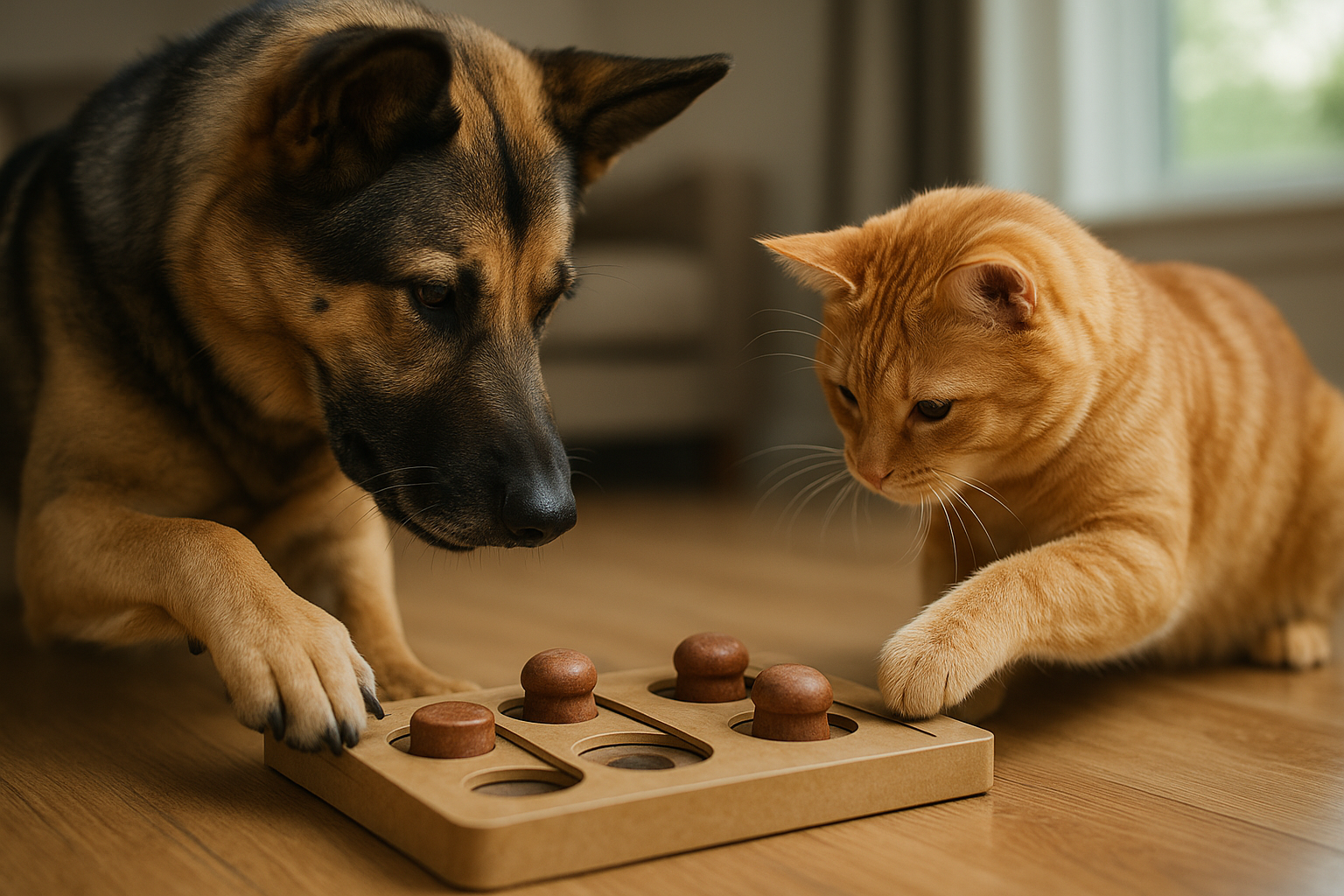
Enrichment and mental exercise benefits
Mental enrichment reduces boredom and problem behaviors that can interfere with leash and recall training. Puzzle feeders, scent games, short training challenges, and supervised play offer cognitive outlets that make dogs more receptive during formal training. Integrating enrichment before walks or sessions can also focus attention; a brief scent search or a food-dispensing toy helps a dog transition from high arousal to a more trainable state. Enrichment ties into grooming and overall care routines by supporting balanced behavior and lowering stress-related resistance during handling.
Exercise, mobility, and physical readiness
A dog’s physical condition affects learning. Regular exercise tailored to breed and age supports mobility and reduces excess energy that can make leash training harder. Consider low-impact options for dogs with mobility concerns and consult your veterinarian about exercise plans that align with diet and wellness needs. Short structured play before recall practice may boost responsiveness, while over-exertion can lower focus. Attention to dental health, parasite prevention, and nutrition ensures dogs feel well enough to participate consistently in training.
Safety considerations during leash and recall training
Safety is central: use secure, well-fitted collars or harnesses and a reliable long line when working at a distance. Be mindful of traffic, other animals, and local wildlife; practice recalls in controlled areas before generalizing to busy public spaces. Teach an emergency recall cue that is distinct from everyday commands and reserve higher-value rewards for that cue. First aid knowledge for pet owners is useful—carry supplies for minor injuries and know how to respond to heat stress or encounters with parasites. Travel preparedness, including restraint and documentation, also supports consistent training while away from home.
Wellness and supporting long-term reliability
Long-term reliability depends on ongoing reinforcement, routine, and attention to overall wellness. Regular veterinary checkups can identify health issues that affect behavior, such as pain or mobility limitations. Maintain a balanced diet and monitor weight, as both can influence energy levels and motivation. Grooming sessions provide handling practice that supports calm responses during walks and training. If adoption history or prior experiences affect behavior, consider structured behavior work or professional support. Training should evolve as your dog ages, adjusting intensity, frequency, and reinforcement types to match mobility and cognitive changes.
Reliable leash and recall behavior emerges from consistent, incremental training built on positive reinforcement, physical care, and mental stimulation. By combining practical teaching progressions with attention to nutrition, exercise, grooming, and safety, owners create the conditions for dependable responses. Expect gradual progress, celebrate small milestones, and adapt strategies to your dog’s individual needs for steady, sustainable results.